An array is defined as the collection of similar type of data items stored at contiguous memory locations. Arrays are the derived data type in C programming language which can store the primitive type of data such as int, char, double, float, etc. It also has the capability to store the collection of derived data types, such as pointers, structure, etc. The array is the simplest data structure where each data element can be randomly accessed by using its index number.
C array is beneficial if you have to store similar elements. For example, if we want to store the marks of a student in 6 subjects, then we don't need to define different variables for the marks in a different subject. Instead of that, we can define an array which can store the marks in each subject at the contiguous memory locations.
By using the array, we can access the elements easily. Only a few lines of code are required to access the elements of the array.
Properties of Array
The array contains the following properties.
- Each element of an array is of the same data type and carries the same size, i.e., int = 4 bytes.
- Elements of the array are stored at contiguous memory locations where the first element is stored at the smallest memory location.
- Elements of the array can be randomly accessed since we can calculate the address of each element of the array with the given base address and the size of the data element.
Advantage of C Array
1) Code Optimization: Less code to access the data.
2) Ease of traversing: By using the for loop, we can retrieve the elements of an array easily.
3) Ease of sorting: To sort the elements of the array, we need a few lines of code only.
4) Random Access: We can access any element randomly using the array.
The disadvantage of C Array
1) Fixed Size: Whatever size, we define at the time of declaration of the array, we can't exceed the limit. So, it doesn't grow the size dynamically like LinkedList which we will learn later.
Declaration of C Array
We can declare an array in the c language in the following way.
data_type array_name[array_size];
Now, let us see the example to declare the array.
int marks[5];
Here, int is the data_type, marks are the array_name, and 5 is the array_size.
Initialization of C Array
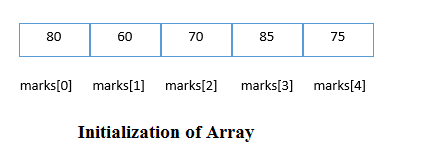
The simplest way to initialize an array is by using the index of each element. We can initialize each element of the array by using the index. Consider the following example.
marks[0]=80;//initialization of array
marks[1]=60;
marks[2]=70;
marks[3]=85;
marks[4]=75;
C array example
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i=0;
int marks[5];//declaration of array
marks[0]=80;//initialization of array
marks[1]=60;
marks[2]=70;
marks[3]=85;
marks[4]=75;
//traversal of array
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("%d \n",marks[i]);
}//end of for loop
return 0;
}
Output
80
60
70
85
75
C Array: Declaration with Initialization
We can initialize the c array at the time of declaration. Let's see the code.
int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60};
In such a case, there is no requirement to define the size. So it may also be written as the following code.
int marks[]={20,30,40,50,60};
Let's see the C program to declare and initialize the array in C.
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i=0;
int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60};//declaration and initialization of array
//traversal of array
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("%d \n",marks[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Output
20
30
40
50
60
C Array Example: Sorting an array
In the following program, we are using the bubble sort method to sort the array in ascending order.
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int i, j,temp;
int a[10] = {10, 9, 7,101, 23,44,12, 78, 34, 23};
for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
for(j = i+1; j<10; j++)
{
if(a[j] > a[i])
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("Printing Sorted Element List ...\n");
for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
printf("%d\n",a[i]);
}
}
Program to print the largest and second largest element of the array.
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int arr[100],i,n,largest,sec_largest;
printf("Enter the size of the array?");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the elements of the array?");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
largest = arr[0];
sec_largest = arr[1];
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(arr[i]>largest)
{
sec_largest = largest;
largest = arr[i];
}
else if (arr[i]>sec_largest && arr[i]!=largest)
{
sec_largest=arr[i];
}
}
printf("largest = %d, second largest = %d",largest,sec_largest);
}





0 comments:
Post a Comment