Why use structure?
In C, there are cases where we need to store multiple attributes of an entity. It is not necessary that an entity has all the information of one type only. It can have different attributes of different data types. For example, an entity Student may have its name (string), roll number (int), marks (float). To store such type of information regarding an entity student, we have the following approaches:
- Construct individual arrays for storing names, roll numbers, and marks.
- Use a special data structure to store the collection of different data types.
Let's look at the first approach in detail.
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
char names[2][10],dummy; // 2-dimensioanal character array names is used to store the names of the students
int roll_numbers[2],i;
float marks[2];
for (i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student %d",i+1);
scanf("%s %d %f",&names[i],&roll_numbers[i],&marks[i]);
scanf("%c",&dummy); // enter will be stored into dummy character at each iteration
}
printf("Printing the Student details ...\n");
for (i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("%s %d %f \n" , names[i] ,roll_numbers[i] ,marks[i]);
}
}
Output
Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 1Arun 90 91
Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 2Varun 91 56
Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 3Sham 89 69
Printing the Student details...
Arun 90 91.000000
Varun 91 56.000000
Sham 89 69.000000
The above program may fulfill our requirement of storing the information of an entity student. However, the program is very complex, and the complexity increase with the amount of the input. The elements of each of the array are stored contiguously, but all the arrays may not be stored contiguously in the memory. C provides you with an additional and simpler approach where you can use a special data structure, i.e., structure, in which, you can group all the information of different data type regarding an entity.
What is Structure
Structure in c is a user-defined data type that enables us to store the collection of different data types. Each element of a structure is called a member. Structures ca; simulate the use of classes and templates as it can store various information
The struct keyword is used to define the structure. Let's see the syntax to define the structure in c.
struct structure_name
{
data_type member1;
data_type member2;
.
.
data_type memeberN;
};
Let's see the example to define a structure for an entity employee in c.
struct employee
{ int id;
char name[20];
float salary;
};
The following image shows the memory allocation of the structure employee that is defined in the above example.
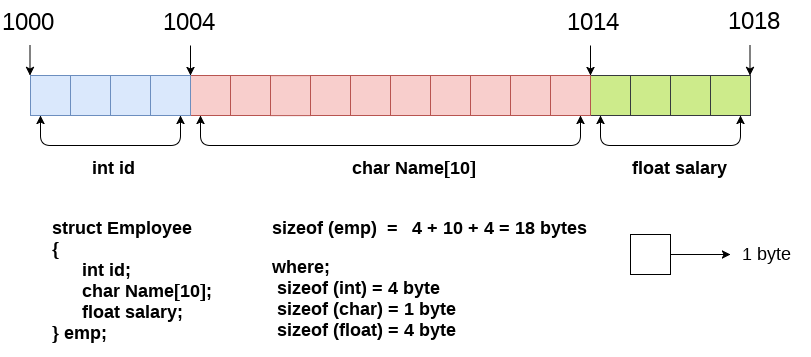
Here, struct is the keyword; employee is the name of the structure; id, name, and salary are the members or fields of the structure. Let's understand it by the diagram given below:
Declaring structure variable
We can declare a variable for the structure so that we can access the member of the structure easily. There are two ways to declare structure variable:
- By struct keyword within main() function
- By declaring a variable at the time of defining the structure.
1st way:
Let's see the example to declare the structure variable by struct keyword. It should be declared within the main function.
struct employee
{ int id;
char name[50];
float salary;
};
Now write given code inside the main() function.
struct employee e1, e2;
The variables e1 and e2 can be used to access the values stored in the structure. Here, e1 and e2 can be treated in the same way as the objects in C++ and Java.
2nd way:
Let's see another way to declare variable at the time of defining the structure.
struct employee
{ int id;
char name[50];
float salary;
}e1,e2;
Which approach is good
If a number of variables are not fixed, use the 1st approach. It provides you the flexibility to declare the structure variable many times.
If no. of variables are fixed, use 2nd approach. It saves your code to declare a variable in main() function.
Accessing members of the structure
There are two ways to access structure members:
- By . (member or dot operator)
- By -> (structure pointer operator)
Let's see the code to access the id member of p1 variable by . (member) operator.
p1.id
C Structure example
Let's see a simple example of structure in C language.
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct employee
{ int id;
char name[50];
}e1; //declaring e1 variable for structure
int main( )
{
//store first employee information
e1.id=101;
strcpy(e1.name, "Sonoo Jaiswal");//copying string into char array
//printing first employee information
printf( "employee 1 id : %d\n", e1.id);
printf( "employee 1 name : %s\n", e1.name);
return 0;
}
Output:
employee 1 id : 101
employee 1 name : Sonoo Jaiswal
Let's see another example of the structure in C language to store many employees information.
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct employee
{ int id;
char name[50];
float salary;
}e1,e2; //declaring e1 and e2 variables for structure
int main( )
{
//store first employee information
e1.id=101;
strcpy(e1.name, "Sonoo Jaiswal");//copying string into char array
e1.salary=56000;
//store second employee information
e2.id=102;
strcpy(e2.name, "James Bond");
e2.salary=126000;
//printing first employee information
printf( "employee 1 id : %d\n", e1.id);
printf( "employee 1 name : %s\n", e1.name);
printf( "employee 1 salary : %f\n", e1.salary);
//printing second employee information
printf( "employee 2 id : %d\n", e2.id);
printf( "employee 2 name : %s\n", e2.name);
printf( "employee 2 salary : %f\n", e2.salary);
return 0;
}
Output:
employee 1 id : 101
employee 1 name : Sonoo Jaiswal
employee 1 salary : 56000.000000
employee 2 id : 102
employee 2 name : James Bond
employee 2 salary : 126000.000000






0 comments:
Post a Comment